In this blog post, we’ll zoom in on one specific Incoterm: CPT (Carriage Paid To). Whether you’re a seasoned importer or just dipping your toes into the waters of international trade, understanding what CPT entails is crucial for successful transactions. So buckle up as we dive into the world of CPT Incoterm and explore its key responsibilities, benefits, limitations, and how it compares with other popular Incoterms. Let’s get started!
What is the CPT Incoterm?
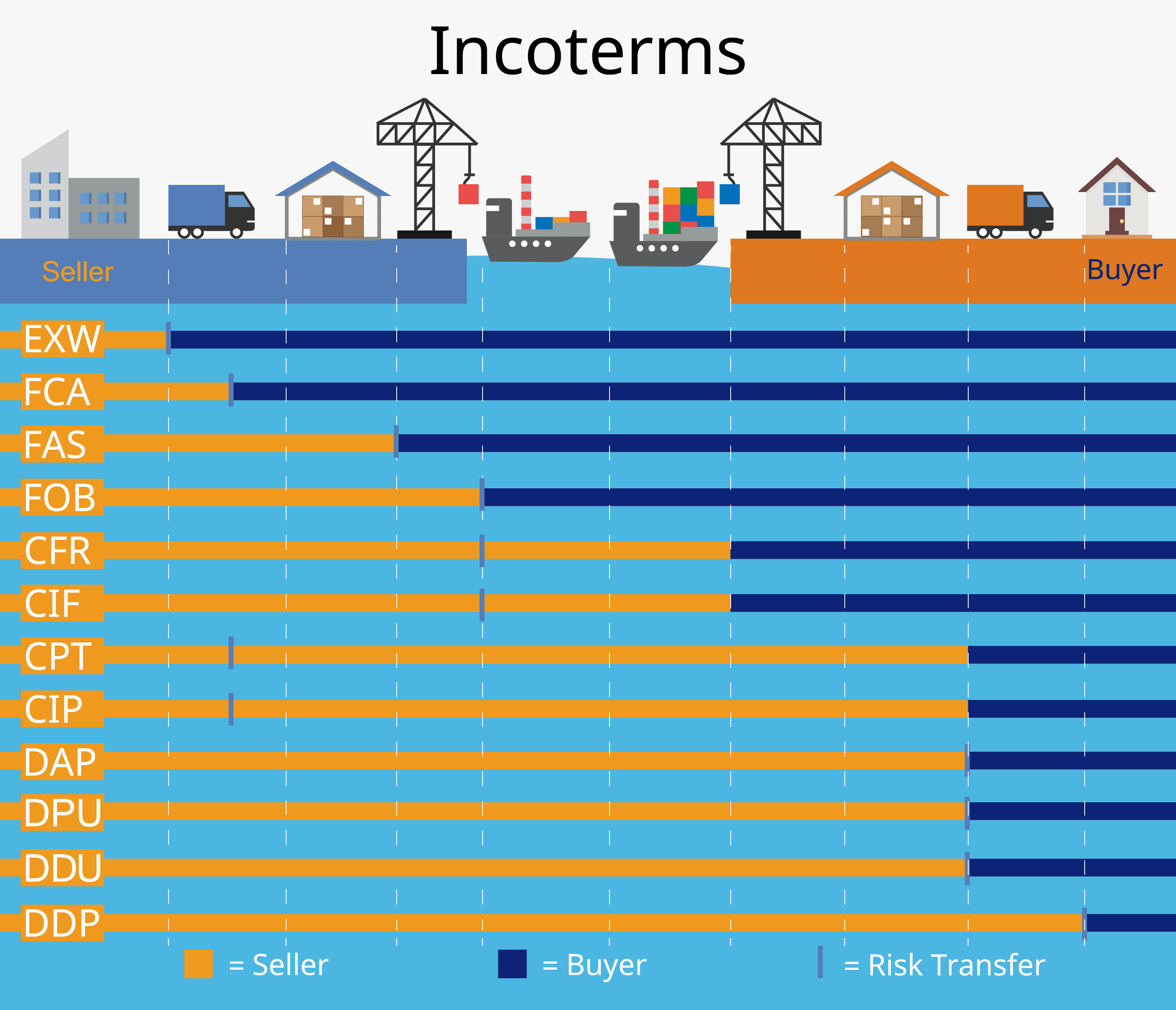
What exactly does the CPT Incoterm mean? Well, it stands for Carriage Paid To, and as the name suggests, it places the responsibility of transportation and delivery on the seller. Under CPT, the seller is responsible for arranging and paying for transportation to a named destination mentioned in the contract.
This means that once the goods are loaded onto the carrier at their place of origin, be it by land, sea, or air, it becomes the seller’s duty to ensure safe passage until they reach their final destination. They must also take care of any necessary export documentation and customs clearance.
However, it’s important to note that while sellers bear these responsibilities during transit, they do not cover insurance costs. That falls under a separate Incoterm called CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To). So if you’re looking for an all-inclusive option that includes insurance coverage as well as transportation costs, CIP might be a better choice.
Understanding what CPT entails is crucial when negotiating international contracts. It ensures clarity regarding who bears responsibility for transporting goods and where those responsibilities shift from one party to another throughout the journey. Now let’s delve further into some key responsibilities buyers and sellers have under CPT Incoterm!
Key Responsibilities of Buyers and Sellers under CPT
When it comes to international trade, understanding the responsibilities of both buyers and sellers is crucial. The Carriage Paid To (CPT) Incoterm outlines these responsibilities clearly, ensuring a smooth transaction process.
For buyers, their main responsibility under CPT is to pay for the goods once they have been delivered to the agreed-upon destination. This means that buyers need to ensure they have the necessary funds ready and available in order to fulfill this obligation. Additionally, buyers are responsible for arranging transportation from the destination port or airport to their chosen location.
On the other hand, sellers have several key responsibilities under CPT as well. They must deliver the goods to an agreed-upon carrier at an agreed-upon place of shipment. This involves taking care of all export customs formalities and providing proper documentation such as commercial invoices and packing lists.
Moreover, sellers are responsible for arranging transportation from the place of shipment to the specified destination. They must also bear any risks and costs associated with delivering the goods until they reach this final destination point.
By clearly defining these responsibilities, CPT provides clarity for both parties involved in international trade transactions. This helps minimize misunderstandings or disputes that can arise during shipping processes.
Understanding and fulfilling one’s obligations under CPT is essential for successful international trades where buyer-seller collaboration is crucially important.
Benefits of Using CPT for International Trade
Using CPT provides clarity and transparency in terms of cost allocation. With this Incoterm, the seller takes responsibility for transportation costs up to the agreed-upon delivery point. This means that buyers have a clear understanding of what costs they will be responsible for beyond that point.
Another advantage of using CPT is that it allows for flexibility in terms of mode of transport. Whether goods are transported by air, sea, road, or rail, CPT can easily accommodate different shipping methods.
Furthermore, CPT eliminates the need for negotiation regarding transportation arrangements. The seller handles all aspects related to transportation and delivery until reaching the agreed-upon destination. This simplifies logistics management and reduces potential disputes between parties.
Using CPT also enables faster customs clearance processes. Since the seller bears responsibility until arrival at the designated location, there is less risk of delays or complications during customs procedures.
Additionally, by utilizing CPT as an Incoterm, both buyers and sellers can benefit from increased control over shipment tracking and monitoring. This helps ensure timely deliveries and minimizes any potential disruptions along the supply chain.
Opting for CPT when engaging in international trade offers numerous advantages that streamline operations while providing peace of mind to both parties involved.

Limitations and Disadvantages of CPT
While the CPT Incoterm can be advantageous for international trade, it is important to be aware of its limitations and disadvantages.
One limitation of using CPT is that it places a significant burden on the seller in terms of transportation costs. The seller is responsible for arranging and paying for carriage to the agreed destination, which can add up quickly depending on the distance and mode of transport. This could potentially eat into their profit margins.
Another disadvantage is that there may be a lack of control over the transportation process. Once the goods have been handed over to the carrier, it becomes their responsibility to ensure safe delivery. If any issues or delays occur during transit, it can cause frustration and inconvenience for both parties involved.
Additionally, with CPT, there is a risk associated with loss or damage to goods during transportation. While insurance coverage may mitigate some of this risk, relying solely on carrier liability may not provide adequate protection in all situations.
Communication between buyer and seller becomes crucial under CPT as they need to coordinate effectively regarding shipment details such as packing requirements, documentation, customs clearance procedures etc., Failure to communicate properly can lead to misunderstandings and potential delays.
While CPT offers certain advantages in terms of cost-sharing between buyer and seller when it comes to transportation expenses,
it’s essential for parties involved in international trade transactions using this incoterm understand its limitations and take necessary precautions accordingly.
Comparison with Other Incoterms
Buyers and sellers have specific responsibilities under CPT. The seller must deliver the goods to a carrier chosen by them, handle export formalities, and bear the cost of transport to the agreed destination. On the other hand, buyers are responsible for unloading costs at their destination country and any import duties or taxes incurred.
However beneficial it may be, there are limitations to using CPT as well. One major disadvantage is that once delivery has been made to the carrier named by the seller, any subsequent loss or damage falls solely on the buyer’s shoulders. This highlights the importance of comprehensive insurance coverage when employing this Incoterm.
In comparison with other Incoterms like CIF (Cost Insurance Freight) or FOB (Free On Board), CPT stands out due to its focus on carriage rather than loading onto vessels or insurance coverage respectively. If you want more control over transportation arrangements while still ensuring risk transfer like CIF but without including insurance costs upfront – then opting for CPT might be your best choice!
Understanding these differences allows businesses to choose an appropriate Incoterm that aligns with their needs while minimizing potential disputes or misunderstandings.