Today, we’re here to shed some light on one of the most commonly used Incoterms – CIF Incoterm (Cost, Insurance and Freight). If you’re ready to dive into the world of global commerce and understand how CIF can impact your business, then grab a cup of coffee and join us as we demystify this powerful term. From its use in international transactions to its advantages and disadvantages, we’ll cover it all! So buckle up and let’s embark on this informative journey together!
Explanation of Cost, Insurance, and Freight
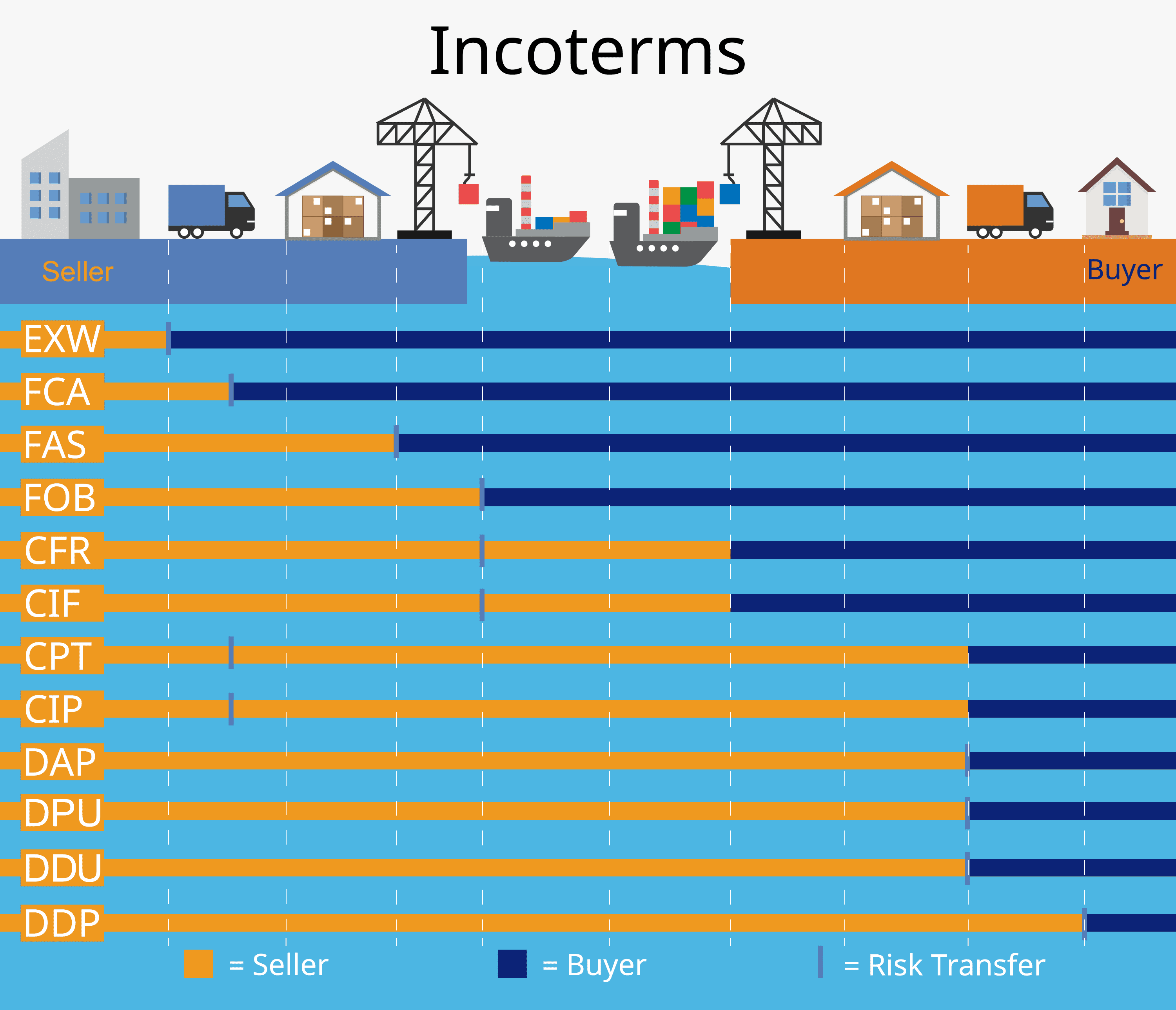
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) is an Incoterm that outlines the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. Let’s break it down to understand its meaning.
Firstly, “cost” refers to the price of the goods being sold. This includes the cost of production, packaging, labeling, and any other expenses incurred by the seller up until the point of shipment.
Secondly, “insurance” ensures that the goods are protected during transit. Under CIF terms, it is typically the seller’s responsibility to arrange insurance coverage for the buyer against loss or damage while in transit.
Lastly, “freight” encapsulates all transportation costs from the seller’s location to a specified destination port or airport. The seller takes on this responsibility as part of their obligation under CIF Incoterm.
In essence, CIF requires sellers to handle not only shipping but also insurance arrangements for their buyers’ peace of mind. By clearly defining these aspects within a transaction agreement using CIF Incoterm, both parties can have a clear understanding of their roles and obligations throughout each stage of shipping.
Use of CIF Incoterm in International Trade
The CIF Incoterm plays a crucial role in international trade, providing clarity and structure to the shipment process. This term is commonly used when the seller takes responsibility for delivering the goods to a specific port of destination.
By using CIF, both buyers and sellers can clearly define their responsibilities and obligations. The cost includes not only the price of the goods themselves but also covers transportation expenses up until they reach the agreed-upon port. Additionally, insurance is provided to protect against any potential damage or loss during transit.
One advantage of using CIF Incoterm is that it relieves buyers from having to worry about arranging transportation and insurance separately. The seller takes on this responsibility, allowing buyers to focus on other aspects of their business operations.
However, there are some disadvantages associated with CIF as well. Since sellers arrange for transportation and insurance, they may have limited control over these processes, which could lead to delays or issues beyond their control. Additionally, buyers may have less visibility into shipping costs since these are bundled together in one upfront payment.
When comparing CIF Incoterm with other options such as FOB (Free On Board) or EXW (Ex Works), it’s important for businesses to consider factors such as risk allocation, cost management, and their own capabilities within the supply chain.
While there are advantages and disadvantages associated with using CIF Incoterm in international trade transactions, its use provides clear guidelines regarding cost allocation and risk transfer between parties involved in a shipment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of using CIF Incoterm
When it comes to international trade, choosing the right Incoterm is crucial for both buyers and sellers. One commonly used option is the CIF Incoterm, which stands for Cost, Insurance, and Freight. While this term may seem convenient at first glance, it also has its advantages and disadvantages.
One advantage of using CIF Incoterm is that it’s a hassle-free option for buyers. With this term, the seller takes care of not only the cost of goods but also the insurance and freight charges until they reach the destination port. This means less paperwork and logistics management for buyers.
Another advantage is that using CIF Incoterm provides a higher level of security for buyers. Since sellers are responsible for insuring the goods during transit, any damage or loss that occurs during transportation will be covered by insurance.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider when using CIF Incoterm. As a buyer relying on this term, you have limited control over selecting your own insurer or carrier since these aspects are handled by the seller.
Additionally, with CIF Incoterm, buyers often end up paying more in terms of insurance premiums compared to if they arranged their own coverage. This can lead to higher costs in the long run.
Furthermore, another disadvantage is that once goods are loaded onto the vessel at origin port under this term; risk transfers from seller to buyer regardless if delivery has taken place yet or not – so any delays or damages during shipping become buyer’s responsibility.
While CIF Incoterm offers convenience and security for buyers in terms of cost management and insurance coverage during transit; it does come with limitations such as limited control over carriers/insurers chosen by sellers leading potentially higher costs due increased premium rates & transfer risks before actual delivery takes place
Comparing CIF Incoterm to other Incoterms
When it comes to choosing the right incoterm for your international trade transactions, it’s essential to consider the specific needs and requirements of your business. While CIF Incoterm offers certain advantages, it may not be the most suitable option in every situation.
One alternative that is often compared to CIF is FOB (Free on Board). Unlike CIF, where the seller takes care of insurance and transportation costs, FOB places these responsibilities on the buyer. This can give buyers more control over these aspects but also means they need to arrange their own insurance coverage.
Another popular incoterm worth considering is EXW (Ex Works), which gives even more control to the buyer. With EXW, the seller only makes goods available at their premises or specified location, leaving all other logistics and costs in the hands of the buyer. This can be advantageous for buyers who have established relationships with reliable shipping agents and prefer being fully responsible for transport arrangements.
It’s important to note that each incoterm has its own set of advantages and disadvantages based on factors such as cost allocation, risk management, and level of control desired by both parties involved in a transaction. Therefore, careful consideration should be given before making a final decision on which incoterm to use.