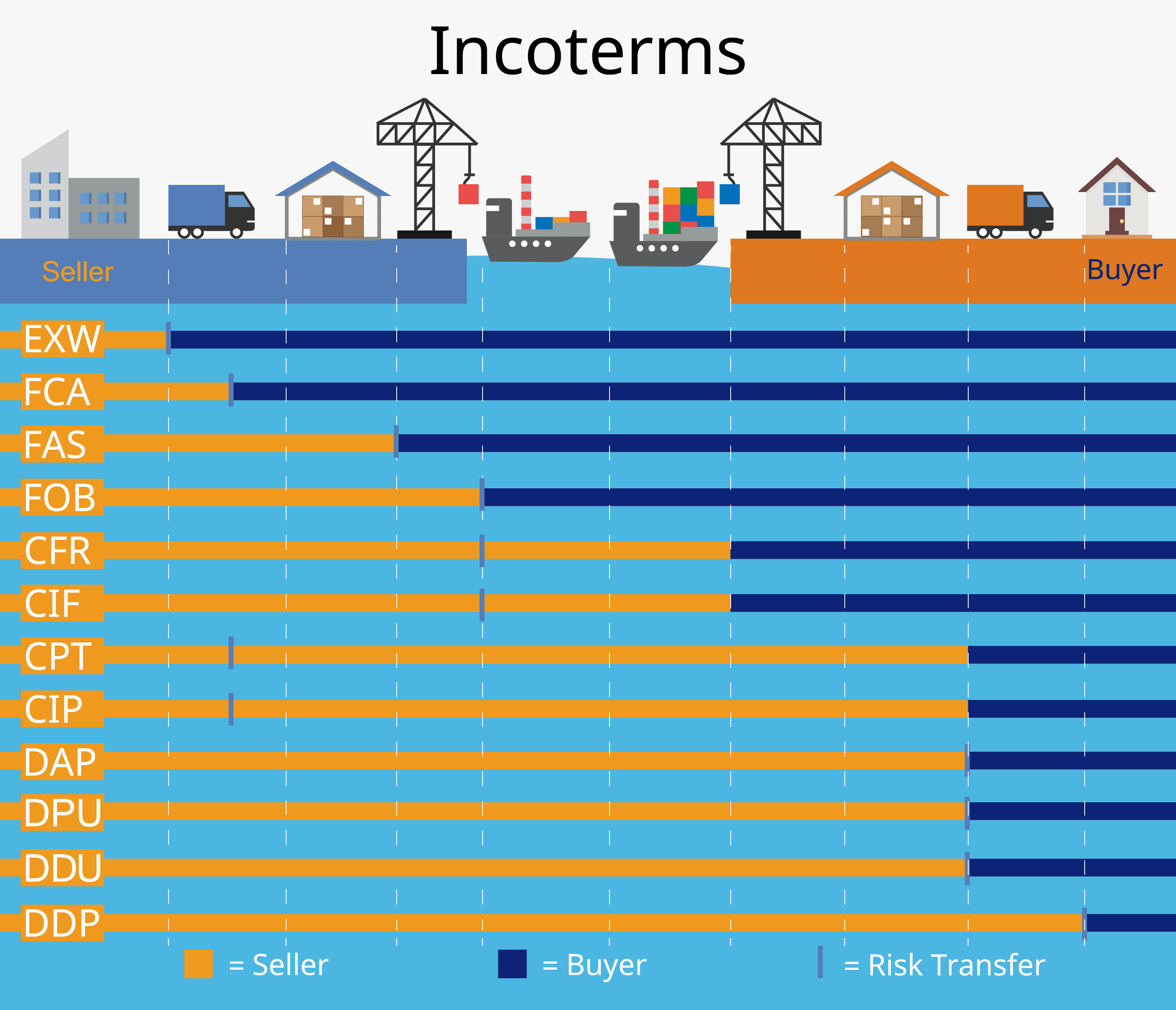
Introduction:
International trade involves a complex network of logistics and procedures that ensure the smooth movement of goods from sellers to buyers. One crucial aspect of this process is understanding Incoterms, which are trade terms and conditions that describe the responsibilities and liabilities between sellers and buyers at different stages of cargo delivery. In this article, we will delve into the basics of Incoterms, focusing on six commonly used terms: Ex Works (EXW), Free On Board (FOB), Cost and Freight (CFR), Cost Insurance and Freight (CIF), Delivered At Place (DAP), and Delivered Duty Paid (DDP).
1. Ex Works (EXW):
Ex-Works refers to a trade condition where sellers hand over the goods to buyers at their factory or exporting location. Buyers are responsible for all transportation costs from the factory to the delivery site, assuming full responsibility for the cargo once it is loaded onto containers. This term places minimal obligations on sellers while transferring maximum liability to buyers.
2. Free On Board (FOB):
Free On Board signifies that sellers bear responsibility for the goods until they are loaded onto vessels at the exporting site. Sellers cover local transportation fees in the exporting country, while buyers assume responsibility for ocean freight charges as well as any additional costs incurred during delivery in importing countries.
3. Cost & Freight (CFR):
Cost & Freight entails that sellers pay all freight expenses from their factory or exporting location to port in importing countries under CFR trade terms. Importers then take charge of shipping fees and transportation costs needed beyond import ports until final delivery destinations.
4. Cost Insurance & Freight (CIF):
Similar to CFR, CIF requires exporters to cover all freight costs up till port arrival in importing countries; however, an essential distinction lies within insurance coverage included by exporters when using CIF terms—ensuring added protection throughout cargo’s journey. Importers are responsible for costs beyond port arrival, including transportation fees and insurance for the cargo.
5. Delivered At Place (DAP):
Delivered At Place states that sellers bear all costs and assume responsibility for goods until they reach a specific delivery location in importing countries. DAP is often referred to as “door-to-door” because it encompasses logistics management from factory or exporting site to designated delivery points in the importer’s country.
6. Delivered Duty Paid (DDP):
Delivered Duty Paid places complete logistical responsibility on exporters or sellers, involving not only delivering cargo to specified locations but also covering import taxes such as custom duties and consumption taxes. In contrast, under DAP terms, importers are accountable for paying these additional charges.
Understanding Cost vs Responsibility:
It is crucial to comprehend both cost allocation and cargo responsibility when dealing with Incoterms:
– EXW shifts most of the burden onto buyers, who handle all aspects of logistics while assuming full liability.
– FOB divides responsibilities between sellers (pre-vessel loading) and buyers (post-vessel loading).
– CFR/CIF transfers liability from sellers to buyers upon vessel loading but handles cost differently: CFR requires importers to cover expenses after unloading at ports; CIF includes insurance arrangements by exporters.
– DAP/DDP place more obligations on sellers by managing logistics throughout the entire journey until final delivery destinations within importing countries.
Importance of Cargo Insurance:
Given the uncertainties inherent in international trade, securing insurance coverage for shipments is highly recommended. Unforeseen events like fires aboard vessels or accidents during handling can lead to significant losses if cargos are uninsured. Therefore, obtaining comprehensive cargo insurance provides peace of mind and safeguards against potential financial setbacks caused by unforeseeable circumstances.
Navigating international trade requires a firm knowledge of Incoterms—trade terms that define responsibilities and liabilities between sellers and buyers during different stages of cargo movement. While there are 11 Incoterms in total, understanding the basics of six commonly used terms (EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, DAP, and DDDP)