
In the dynamic world of international trade, understanding the import and export activities of a country can provide invaluable insights for logistics providers, freight forwarders, and businesses involved in global commerce. New Zealand, known for its stunning landscapes and vibrant agriculture, plays a significant role in the global market. This blog post will take you through New Zealand’s main exports and imports, offering a detailed analysis to help you better understand this crucial part of the world economy.
Main Exports of New Zealand 1. Dairy Products
1. Dairy Products
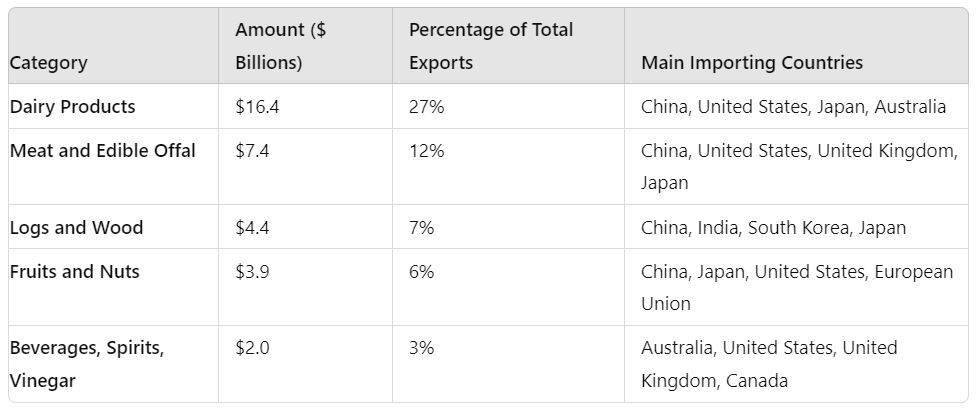
New Zealand’s dairy exports are a powerhouse in the global market, valued at approximately $16.4 billion. This sector represents around 27% of the country’s total exports. Key destinations for these exports include China, the United States, Japan, and Australia.
New Zealand is among the world’s leading producers of dairy products, particularly milk powder, butter, and cheese. The industry is not just a significant contributor to GDP but also supports rural communities and stimulates economic growth through international trade. The country’s commitment to high-quality production standards has cemented its reputation in these markets.
2. Meat and Edible Offal
Meat and edible offal exports are another significant sector, generating around $7.4 billion and making up about 12% of New Zealand’s total exports. Major importing countries include China, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan.
New Zealand’s meat industry is globally renowned for its high-quality lamb, beef, and venison. The sector’s emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices enhances its competitiveness. Consumers worldwide trust New Zealand meat products, making them a staple in many international markets.
3. Logs and Wood
Logs and wood exports are vital to New Zealand’s economy, contributing approximately $4.4 billion and accounting for 7% of the nation’s total exports. Key importers include China, India, South Korea, and Japan.
The forestry industry in New Zealand is a crucial driver of employment and regional development. Sustainable forest management practices ensure a steady supply of timber, meeting the growing global demand while preserving natural resources. This balance between supply and sustainability helps solidify New Zealand’s position in the global market.
 4. Fruits and Nuts
4. Fruits and Nuts
Fruits and nuts, especially kiwifruit and apples, are significant export categories, bringing in around $3.9 billion annually, which represents about 6% of New Zealand’s total exports. The primary destinations for these exports are China, Japan, the United States, and the European Union.
New Zealand’s horticulture sector is known for its premium quality produce. The kiwifruit industry, in particular, has seen remarkable growth, with New Zealand being the world’s leading exporter of this fruit. This focus on quality and innovation within the horticulture sector has helped New Zealand strengthen its market presence.
5. Beverages, Spirits, and Vinegar
Beverages, spirits, and vinegar exports, particularly wine, contribute about $2 billion to New Zealand’s export earnings, making up 3% of total exports. Major importing countries include Australia, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.
New Zealand’s wine industry, especially its Sauvignon Blanc, has gained international acclaim. This sector plays a crucial role in promoting the New Zealand brand globally, enhancing tourism and cultural exchange. The wine industry’s focus on quality and sustainability continues to drive its success.
Strategy and Analysis of New Zealand Exports
New Zealand’s export strategy leverages its strengths in agriculture and sustainable practices. The country’s reputation for high-quality products and ethical production methods appeals to global consumers. Exporters must continue to innovate and maintain high standards to sustain growth in these markets.
Main Imports of New Zealand 1. Vehicles
1. Vehicles
Vehicle imports are a major component of New Zealand’s economy, totaling approximately $6.8 billion and accounting for about 12% of the country’s total imports. Key suppliers include Japan, the European Union, Thailand, and Australia.
The majority of these imports consist of cars, trucks, and other transport vehicles. The demand for vehicles is driven by New Zealand’s reliance on road transport and the preference for personal vehicles. This sector’s significance in the import portfolio highlights its importance in supporting both personal and commercial mobility.
2. Machinery and Mechanical Appliances
Imports of machinery and mechanical appliances are vital to New Zealand’s industrial and agricultural sectors, amounting to around $5.8 billion and representing 10% of total imports. Key suppliers include China, the United States, Japan, and Germany.
These imports are crucial for supporting New Zealand’s manufacturing, construction, and farming industries. They include items such as agricultural machinery, industrial equipment, and household appliances, which are essential for the country’s economic activities. The continued import of machinery and mechanical appliances underscores the need for advanced technology to drive productivity.
3. Mineral Fuels and Oils
Mineral fuels and oils, including crude oil, are critical imports for New Zealand, valued at approximately $5.3 billion, making up 9% of total imports. Major suppliers are Australia, Singapore, the United Arab Emirates, and Malaysia.
New Zealand relies heavily on imported fuels for energy production, transportation, and industry. The country’s limited domestic oil production necessitates these imports to meet its energy needs and maintain economic stability. Securing a steady supply of these resources is crucial for sustaining industrial and economic activities.
 4. Electrical Machinery and Equipment
4. Electrical Machinery and Equipment
Electrical machinery and equipment imports play a significant role in New Zealand’s economy, valued at about $4.2 billion, or 7% of total imports. China, the United States, Japan, and South Korea are the leading suppliers.
These imports include a wide range of products, from consumer electronics like smartphones and computers to industrial electrical equipment. The growing demand for technology and electronic devices in both personal and business contexts drives this sector’s importance. Staying at the forefront of technological advancements is essential for New Zealand’s economic growth.
5. Plastics and Plastic Articles
New Zealand imports a substantial amount of plastics and plastic articles, totaling around $2.3 billion and representing 4% of the country’s total imports. China, Australia, the United States, and South Korea are the main suppliers.
Plastics are used extensively across various industries in New Zealand, including packaging, construction, and manufacturing. The high demand for these materials underscores their importance in the country’s import portfolio. Efficient management of plastic imports is vital for supporting various industrial activities.
Strategy and Analysis of New Zealand Imports
New Zealand’s import strategy focuses on securing essential goods and technologies that support its industrial and economic activities. Diversifying sources and maintaining strong trade relationships are key components of this strategy. Importers must stay attuned to global market trends and supply chain dynamics to ensure stability and efficiency.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Understanding the main exports and imports of New Zealand offers valuable insights into the country’s economic landscape. For logistics providers, freight forwarding companies, importers, exporters, and related industry professionals, this knowledge is crucial for optimizing operations and identifying new opportunities.
New Zealand’s commitment to quality and sustainability in its export sectors, combined with its strategic approach to securing essential imports, underscores its resilience and adaptability in the global market. Staying informed about these trade activities can help businesses better navigate the complexities of international commerce and achieve success in their ventures.
Explore more about New Zealand’s trade activities and how they can impact your business by staying connected with our expert insights and updates.




 1. Dairy Products
1. Dairy Products 4. Fruits and Nuts
4. Fruits and Nuts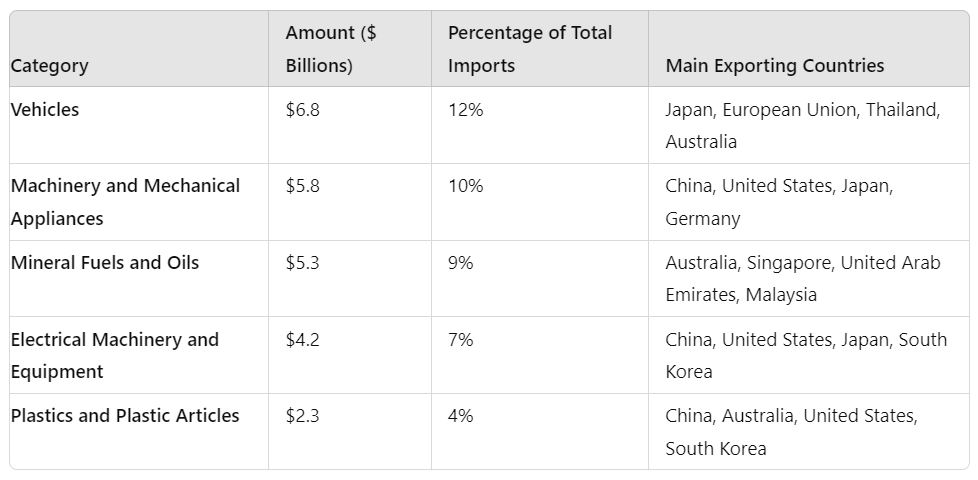 1. Vehicles
1. Vehicles 4. Electrical Machinery and Equipment
4. Electrical Machinery and Equipment Conclusion
Conclusion



