
Understanding a country’s trade dynamics is crucial for businesses involved in logistics, manufacturing, and e-commerce. These insights help stakeholders make informed decisions and identify new opportunities.
Overview of Canada’s Trade Landscape
Canada’s trade landscape is both diverse and robust, driven by its vast natural resources and advanced manufacturing capabilities. The country’s trade policies aim to balance resource optimization with technological growth. This dual approach maintains Canada’s competitive edge in the global market. Below, we explore the main exports and imports of Canada, providing detailed insights and key statistics.
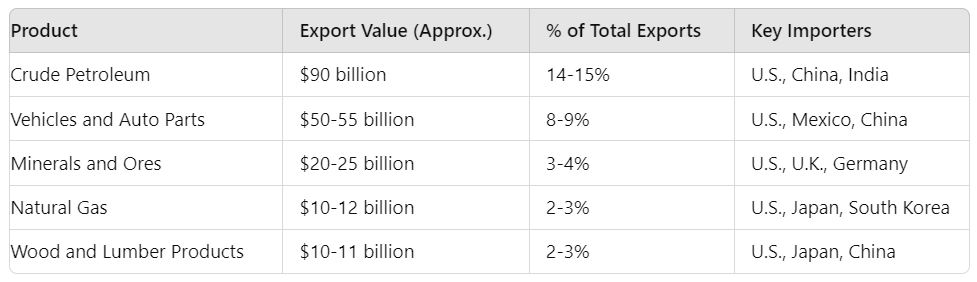
Main Exports of Canada
1. Crude Petroleum
- Export Value: Approx. $90 billion (varies yearly)
- Percentage of Total Exports: 14-15%
- Major Importing Countries: United States, China, India
- Canada is one of the largest exporters of crude oil globally, with the majority of its exports destined for the U.S., due to proximity and trade agreements.
2. Vehicles and Auto Parts
- Export Value: Approx. $50-55 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 8-9%
- Major Importing Countries: United States, Mexico, China
- Canada has a strong automotive manufacturing sector, primarily in Ontario, which is closely integrated with the U.S. auto industry.
 3. Minerals and Ores (Gold, Copper, Iron)
3. Minerals and Ores (Gold, Copper, Iron)
- Export Value: Approx. $20-25 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 3-4%
- Major Importing Countries: United States, United Kingdom, Germany
- Canada is a major exporter of minerals like gold, copper, and iron ore, largely due to its vast natural resources.
4. Natural Gas
- Export Value: Approx. $10-12 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 2-3%
- Major Importing Countries: United States, Japan, South Korea
- Canada is a key global player in natural gas exports, with most of the output going to the United States.
5. Wood and Lumber Products
- Export Value: Approx. $10-11 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 2-3%
- Major Importing Countries: United States, Japan, China
- Canada’s forestry industry is a significant contributor to its export economy, with wood and lumber products being in high demand, especially in the U.S. housing market.
Strategy and Analysis of Canada’s Exports
Canada’s export strategy is driven by resource optimization, market diversification, and technological advancement. By leveraging its vast natural resources and focusing on high-value sectors like energy, minerals, and manufacturing, Canada maintains a strong presence in the global market. The country’s commitment to sustainable resource management and innovation in production ensures that its exports remain competitive, supporting economic growth while adapting to changing global demands. This strategy not only strengthens trade relationships but also positions Canada as a key player in the evolving international trade landscape.
Main Imports of Canada
1. Motor Vehicles and Parts
- Import Value: Approx. $75-80 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 12-13%
- Major Exporting Countries: United States, Mexico, Japan
- Canada heavily relies on imports of motor vehicles and parts, particularly from the U.S. and Mexico, due to the interconnected North American automotive industry.
2. Refined Petroleum
- Import Value: Approx. $20-25 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 4-5%
- Major Exporting Countries: United States, Saudi Arabia, Netherlands
- Despite being a major crude oil producer, Canada imports refined petroleum products to meet domestic fuel demands, especially in regions that lack refining capacity.
3. Electronic and Electrical Equipment
- Import Value: Approx. $30-35 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 6-7%
- Major Exporting Countries: China, United States, Mexico
- Canada imports a large quantity of electronics and electrical machinery, including computers, smartphones, and other high-tech devices, primarily from Asia and the U.S.
 4. Machinery and Equipment
4. Machinery and Equipment
- Import Value: Approx. $50-55 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 8-9%
- Major Exporting Countries: United States, Germany, China
- Machinery, including industrial equipment, engines, and turbines, plays a critical role in supporting Canada’s manufacturing and resource extraction industries.
5. Pharmaceutical Products
- Import Value: Approx. $15-20 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 3-4%
- Major Exporting Countries: United States, Switzerland, Germany
- Canada imports a significant volume of pharmaceutical products, such as medicines and vaccines, to meet healthcare demands, primarily from the U.S. and Europe.
Strategy and Analysis of Canada’s Imports
Canada’s import strategy is centered on securing vital goods and materials to support its diverse economy. By importing essential products such as motor vehicles, machinery, and refined petroleum, Canada ensures the smooth functioning of its key industries, from manufacturing to energy. This strategy is crucial for maintaining economic stability and meeting domestic demand. Additionally, Canada emphasizes the importance of strong trade partnerships with countries like the United States, China, and Mexico, ensuring a reliable supply of high-quality goods that contribute to the nation’s growth and global competitiveness.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Understanding Canada’s main exports and imports provides valuable insights for businesses involved in international trade. Canada’s focus on leveraging natural resources, maintaining sustainable practices, and fostering solid trade relationships keeps it competitive. For freight forwarding companies, logistics providers, importers, exporters, and others in the industry, these insights can guide strategic decision-making and operational planning.
To explore further, consider the data trends and market analyses that continuously shape Canada’s trade landscape. Engage with industry experts and leverage advanced tools to stay ahead in this dynamic field.



 3. Minerals and Ores (Gold, Copper, Iron)
3. Minerals and Ores (Gold, Copper, Iron)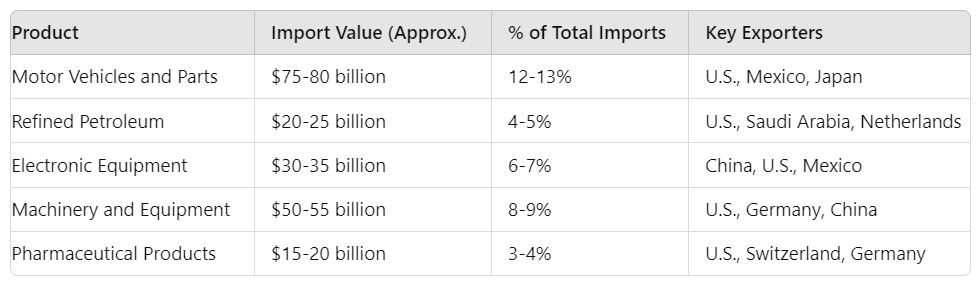
 4. Machinery and Equipment
4. Machinery and Equipment Conclusion
Conclusion



